📚 Introduction
GIS Substations (Gas Insulated Substations) are transforming modern power distribution with their compactness, reliability, and safety. They offer smart solutions for urban, industrial, and offshore projects where space and reliability are critical. Understanding of these modern substations is essential for engineers, project developers, and decision-makers in the power sector.
In this blog, you will explore what GIS substations are, their advantages, major components, and key applications in today’s power infrastructure.

✅ What is a GIS Substation?
A Gas Insulated Substation (GIS) is a compact, high-voltage substation where equipment like circuit breakers and busbars are enclosed within a sealed system filled with sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) gas. This gas offers excellent insulation and arc-quenching properties.
Unlike Air Insulated Substations (AIS), GIS substations save space, improve reliability, and offer better environmental protection.
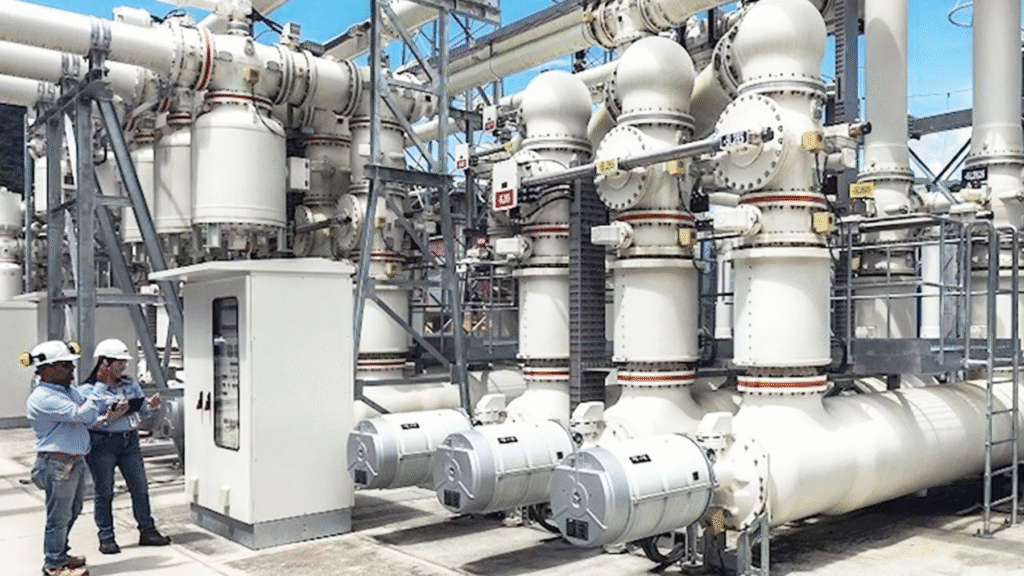

🌟 Advantages of GIS Substations
1. Space-Saving Design
These systems require up to 70% less space compared to AIS. This makes them ideal for cities, tunnels, offshore platforms, and industrial complexes.
2. High Reliability
Since the equipment is enclosed, it is protected from dust, pollution, and moisture, ensuring long-term reliability.
3. Enhanced Safety
The sealed system minimizes risks of accidental contact and arc flashes, creating a safer working environment.
4. Low Maintenance
GIS equipment requires less maintenance due to its enclosed, durable construction.
5. Environmental Flexibility
GIS substations perform well in harsh weather conditions, polluted environments, and coastal regions.
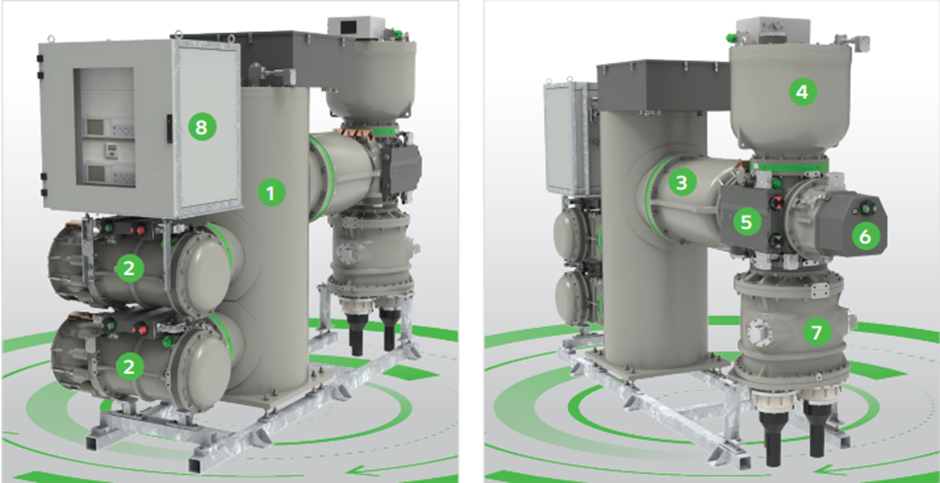
🛠️ Major Components of GIS Substations
The key components include:
- Circuit Breakers (CB): Interrupt fault currents safely.
- Disconnectors (Isolators): Isolate equipment for maintenance.
- Current Transformers (CT) & Potential Transformers (PT): Measure current and voltage.
- Busbars: Conduct power within the substation.
- Gas-Insulated Switchgear (GIS Panels): Compact switchgear units with multiple functions.
- SF6 Gas: Provides insulation and arc-quenching.
- Control & Protection Systems: Ensure safety and automate operations.

🌐 Applications of GIS Substations
These substations are widely used in:
- Urban Substations: Where space is limited.
- Underground and Tunnel Substations: For metro and rail projects.
- Industrial Facilities: Where reliability is crucial.
- Offshore Platforms: Compact and corrosion-resistant.
- High Voltage Substations: Require reduced footprint and high reliability.
⚡ Why GIS Substations Are the Future
Such substations are rapidly gaining popularity as they solve multiple space, safety, and maintenance challenges. They are the future for power distribution in urban and industrial sectors. Additionally, their ability to handle harsh environments makes them a preferred choice for modern power networks.
📅 Best Practices to Remember
- Start site planning early to fit GIS layouts efficiently.
- Always follow SF6 handling and safety guidelines.
- Prioritize reliable OEMs and strict factory testing.
🔗 Related Blogs
- ⚡ Key Differences Between GIS and AIS Substations: A Comparative Guide
- ⚡ When and Why to Choose GIS Substations for Power Projects
💬 Final Thoughts
They are not just a modern option—they are a smart investment in reliable, compact, and low-maintenance power distribution. Understanding their components and applications will help you plan future-ready power infrastructure.
Need help with GIS substation planning? Contact our experts for tailored solutions.
📧 Contact us at: tech@ihpcindia.com