Introduction
In modern power transmission and distribution, Gas Insulated Substations (GIS) are becoming increasingly popular for their compact design and reliability. But the key question for project planners and engineers is: When to choose GIS Substation instead of traditional Air Insulated Substations (AIS)?
In this article, we’ll explore the specific conditions where GIS substations are the best choice and why they provide unmatched advantages in certain projects.
Related reading: GIS Substations: Key Advantages & Applications
1. Why Consider GIS Substations?🛠️
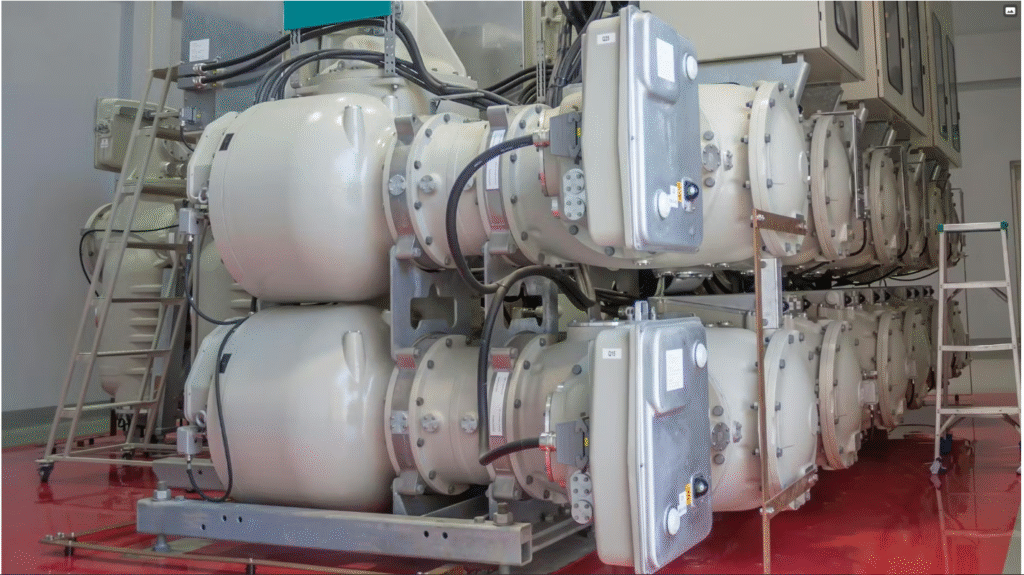
GIS substations use SF₆ gas insulation, offering a space-efficient, safer, and weather-proof solution compared to AIS. Their benefits include:
- Compact Design: Up to 70% less space than AIS.
- High Reliability: Reduced outages due to enclosed equipment.
- Low Maintenance: Minimal exposure to environmental conditions.
- Enhanced Safety: Fully sealed systems reduce accident risks.
Compare advantages here: Key Differences Between GIS and AIS Substations
2. When to Choose GIS Substations🌍
a) Space Constraints
Ideal for urban areas, industrial complexes, and offshore platforms where land cost is high or space is limited.

b) Harsh Environmental Conditions
Perform well in coastal, dusty, or high-pollution zones, where AIS would require frequent cleaning and maintenance.
c) High Voltage and Reliability Needs
Suitable for 110 kV to 400 kV projects demanding continuous power supply and minimal downtime.
d) Strategic Installations
Preferred for critical facilities like data centers, airports, and metros, where uninterrupted power is essential.
3. Why Not Always Choose GIS?💰
While GIS offers many benefits, it comes with higher upfront costs and longer installation times due to specialized equipment. For projects with abundant space and lower budget constraints, AIS might be more practical.
4. Real-World Example🏢
For instance, many data centers in India are now adopting GIS substations due to tight land availability and the need for high reliability in continuous operations.
- A Datacenter in Mumbai installed Asia’s largest Gas Insulated Substation (GIS) dedicated to a data center campus. It initially supports 300 MW, scalable up to 700 MW.
- This GIS powers a two-million-square-foot campus spanning 10 data centers, of which 4 are Tier-4 operational.
▶️ Space Savings
- Compared to a conventional Air Insulated Substation (AIS), the GIS occupies only about 10% of the land area. That translates to significant savings in land cost and footprint footprint optimization in urban environments.
▶️ Reliability & Cost Factors
- Built on a three-line configuration (N+N+1) with multiple diversified power paths to ensure 100% uptime for mission-critical infrastructure.
- The GIS facility features low environmental sensitivity, is seismic-resistant, and requires minimal maintenance—often no major maintenance for up to 25 years, enhancing long-term cost efficiency.
(Reference – new.abb.com+10pv-magazine-india.com+10dqindia.com+10)
✅ Why This Example Highlights GIS Benefits
- Space Constraint Solution
Urban data centers often have very limited land. Here, the GIS allowed the Data Centre Player to fit a multi-hundred-megawatt substation in minimal space, while traditional AIS would have required exponentially more land. - High Capacity & Scalability
Starting with 300 MW and planning for up to 700 MW without geographic expansion makes it ideal for hyperscale growth. - Reliability & Low OPEX
Designed for continuous uptime with built-in redundancy and sealed equipment, minimizing maintenance and operational risk—a critical factor for data center service-level agreements (SLAs).
Conclusion✍️
When to choose GIS substation depends on factors like your project’s space limitations, reliability needs, and environmental conditions. Although GIS solutions involve a higher initial cost, they deliver compact, safe, and efficient power distribution, making them the ideal choice for mission-critical and urban power projects.